How to merge PDFs using JavaScript
Table of contents
Merge multiple PDF files using our merge PDF JavaScript API. Create a free account, get API credentials, and implement merging using Node.js with axios and form-data. Combine with 30+ other API tools for document processing workflows.
In this post, you’ll learn how to combine multiple PDF files using our merge PDF JavaScript API. With our API, you receive 200 credits with the free plan. Different operations on a document consume different amounts of credits, so the number of PDF documents you can generate may vary. You’ll just need to create a free account(opens in a new tab) to get access to your API key.
Nutrient DWS Processor API
Document merging is just one of our 30+ PDF API tools. You can combine our merging tool with other tools to create complex document processing workflows, such as:
- Converting MS Office files and images into PDFs before merging
- Performing OCR on several documents before merging
- Merging, watermarking, and flattening PDFs
Once you create your account, you’ll be able to access all our PDF API tools.
Step 1 — Creating a free account on Nutrient
Go to our website(opens in a new tab), where you’ll see the page below, prompting you to create your free account.
Once you’ve created your account, you’ll be welcomed by the page below, which shows an overview of your plan details.
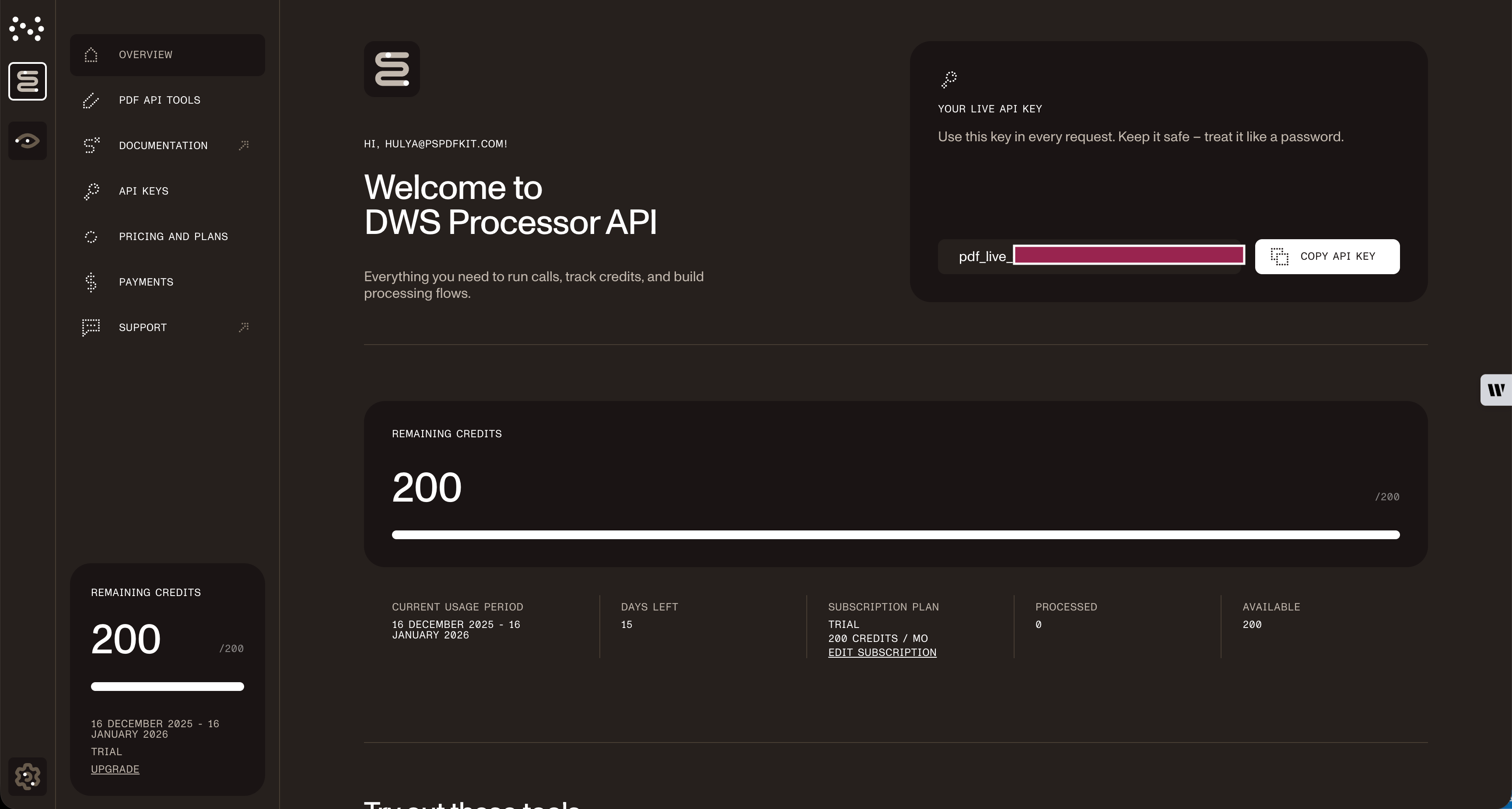
As you can see in the bottom-left corner, you’ll start with 200 credits to process, and you’ll be able to access all our PDF API tools.
Copy the Live API key, because you’ll need this for the merge PDF API.
Step 2 — Setting up files and folders
Now, create a folder called merge_pdf and open it in a code editor. For this tutorial, you’ll use VS Code as your primary code editor. Next, create two folders inside merge_pdf and name them input_documents and processed_documents.
Then, in the root folder, merge_pdf, create a file called processor.js. This is where you’ll keep your code.
Step 3 — Installing dependencies
To get started merging PDF pages, you first need to install the following dependencies:
- axios(opens in a new tab) — This package is used for making REST API calls.
- Form-Data(opens in a new tab) — This package is used for creating form data.
Use the commands below to install both of them:
npm install form-datanpm install axiosStep 4 — Writing the code
Now, open the processor.js file and paste the code below into it:
// This code requires Node.js. Do not run this code directly in a web browser.
const axios = require("axios");const FormData = require("form-data");const fs = require("fs");
const formData = new FormData();formData.append( "instructions", JSON.stringify({ parts: [ { file: "first_half", }, { file: "second_half", }, ], }),);formData.append( "first_half", fs.createReadStream("input_documents/first_half.pdf"),);formData.append( "second_half", fs.createReadStream("input_documents/second_half.pdf"),)(async () => { try { const response = await axios.post( "https://api.nutrient.io/build", formData, { headers: formData.getHeaders({ Authorization: "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY_HERE", }), responseType: "stream", }, );
response.data.pipe( fs.createWriteStream("processed_documents/node_result.pdf"), ); } catch (e) { const errorString = await streamToString(e.response.data); console.log(errorString); }})();
function streamToString(stream) { const chunks = []; return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { stream.on("data", (chunk) => chunks.push(Buffer.from(chunk))); stream.on("error", (err) => reject(err)); stream.on("end", () => resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks).toString("utf8"))); });}Make sure to replace YOUR_API_KEY_HERE with your API key.
Code explanation
You first imported all the packages needed to make the API call, and then you prepared the FormData. After that, you appended the first_half and second_half by reading the first_half.pdf and second_half.pdf files from the input_documents folder.
You then made an asynchronous API call to the merge PDF API and stored the result in processed_documents/node_result.pdf.
Step 5 — Output
To run the code, use the command below:
node processor.jsOn the successful execution of the code, you’ll see a new processed file named node_result.pdf in the processed_documents folder.
The folder structure will look like this:
merge_pdf├── input_documents| └── first_half.pdf| └── second_half.pdf├── node_modules├── processed_documents| └── node_result.pdfYou can now easily integrate this function into your other JavaScript modules and merge different documents.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to merge files for your JavaScript application into a single PDF using our merge PDF API.
If you have a more complex use case, you can use our other tools to add watermarks, perform OCR, and edit (split, flatten, delete, duplicate) documents — and you can even combine these tools. To get started with a free trial, sign up here(opens in a new tab).
Additional resources
Explore more ways to work with Nutrient API:
- Postman collection — Test API endpoints directly in Postman
- Zapier integration — Automate document workflows without code
- MCP Server — PDF automation for LLM applications
- JavaScript client — Official JavaScript library
FAQ
Nutrient DWS Processor API offers 30+ PDF operations, including splitting, watermarking, OCR, flattening, and converting Office documents to PDF. You can combine these operations in a single workflow. For example, merge multiple PDFs, watermark the result, then flatten it to prevent editing — all through the same API.
This code is designed for Node.js only, as indicated by the comment in the code. It uses Node.js modules like fs (file system) and FormData that aren’t available in web browsers. For browser-based PDF merging, you’ll need to implement a server-side endpoint that handles the API call, or use Nutrient’s client-side SDK for in-browser PDF operations.
The code example includes error handling with a try-catch block. When an error occurs, the streamToString function converts the error response into a readable string and logs it. Common errors include invalid API keys, missing files, or malformed instructions. Check the error message for specific details, and ensure your API key is correct and files exist in the specified paths.
The Nutrient DWS Processor API can convert various formats to PDF before merging, including MS Office documents (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) and images (JPEG, PNG, TIFF). First convert documents to PDF using the API’s conversion tools, and then merge them. This enables you to combine mixed document types into a single PDF output.
Instead of using fs.createReadStream() with local file paths, you can fetch remote PDFs and append them as buffers or streams. Use axios to download the PDF, and then append the response data to FormData. For example: const response = await axios.get(url, {responseType: 'stream'}), then formData.append('file', response.data). This allows merging PDFs from remote servers without saving them locally first.