How to convert Excel to PDF using Java
Table of contents
Convert Excel files to PDF using Nutrient’s XLSX-to-PDF Java API. Create a free account, get API credentials, and implement conversion using OkHttp and JSON libraries. Combine with 30+ other API tools for merging, OCR, watermarking, and page manipulation.
Convert Excel files to PDFs in your Java application using Nutrient’s XLSX-to-PDF Java API. Start with 200 free credits — no payment required. Different operations consume different amounts of credits. Create a free account(opens in a new tab) to get your API key.
Why convert Excel to PDF?
Converting Excel files to PDF is essential for workflows requiring document standardization and sharing. Common use cases include:
- Document preservation — Convert spreadsheets to PDFs to preserve formatting, formulas, and layouts regardless of software or device used to view them.
- Professional reporting — Generate polished financial reports, invoices, and data summaries that maintain consistent appearance across platforms.
- Compliance and archiving — Create tamper-resistant records for auditing, regulatory compliance, and long-term document storage.
- Universal sharing — Share data with stakeholders who don’t have Excel or prefer read-only formats that prevent accidental editing.
- Print-ready documents — Ensure spreadsheets print exactly as intended without pagination or formatting issues.
The Excel-to-PDF API automates this process in your workflow.
Nutrient DWS Processor API
Converting Excel to PDF is one of 30+ operations available through our PDF API tools. Combine Excel-to-PDF conversion with other tools for complex workflows:
- Converting various file formats and consolidating them into PDFs
- Converting Excel files and then watermarking and flattening the PDFs
- Processing multiple Excel files before merging them into a single PDF
Your account includes access to all PDF API tools.
Step 1 — Creating a free account on Nutrient
Go to our website(opens in a new tab) to create your free account.
After creating your account, the dashboard shows your plan details.
You start with 200 credits and can access all PDF API tools.
Step 2 — Obtaining the API key
After verifying your email, get your API key from the dashboard. In the menu on the left, click API keys to view your keys.
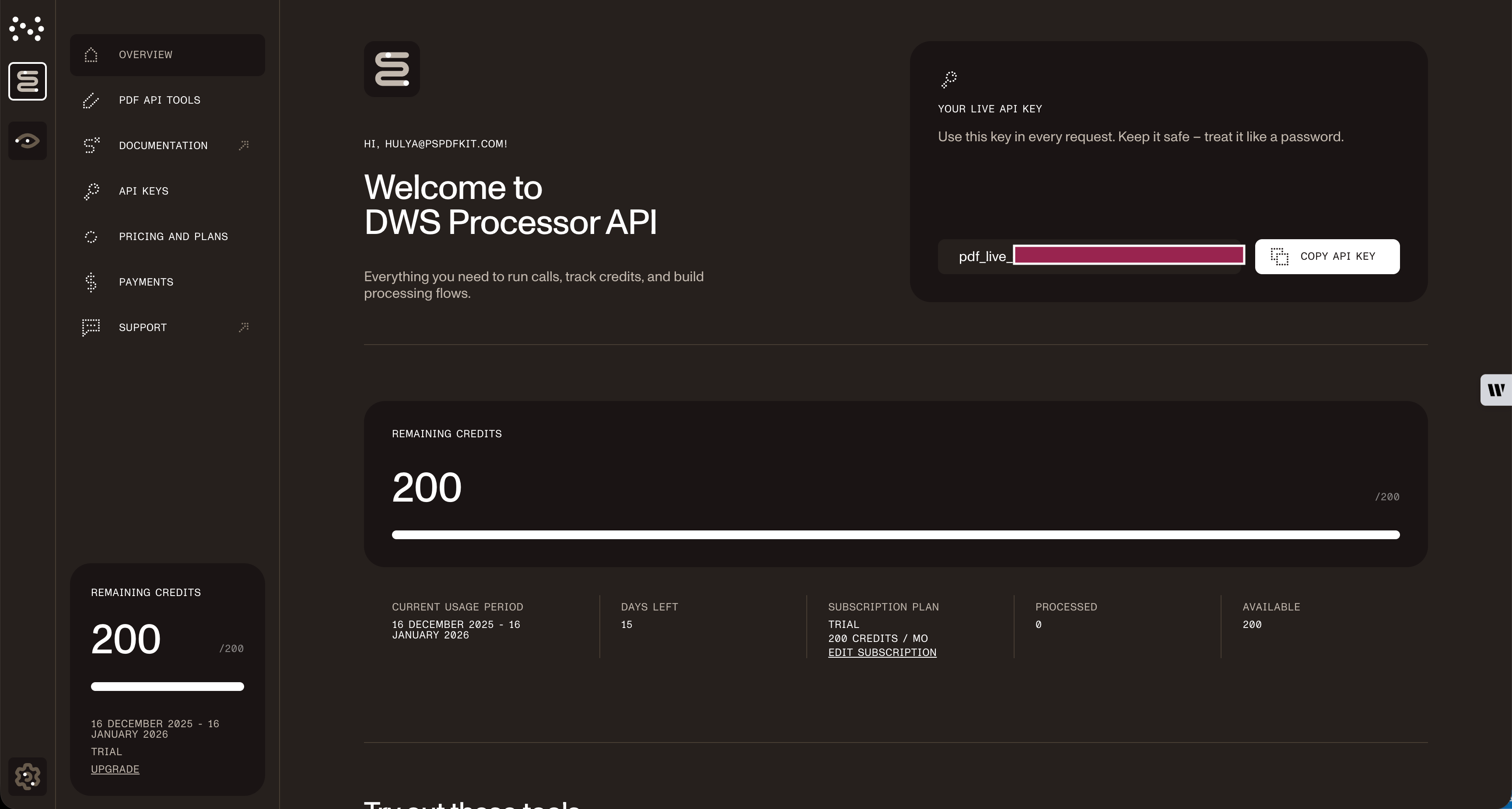
Copy the Live API key for the Excel-to-PDF API.
Step 3 — Setting up folders and files
For this tutorial, use IntelliJ IDEA as your code editor. Create a new project called excel_to_pdf. You can choose any location, but select Java as the language, Gradle as the build system, and Groovy as the Gradle DSL.
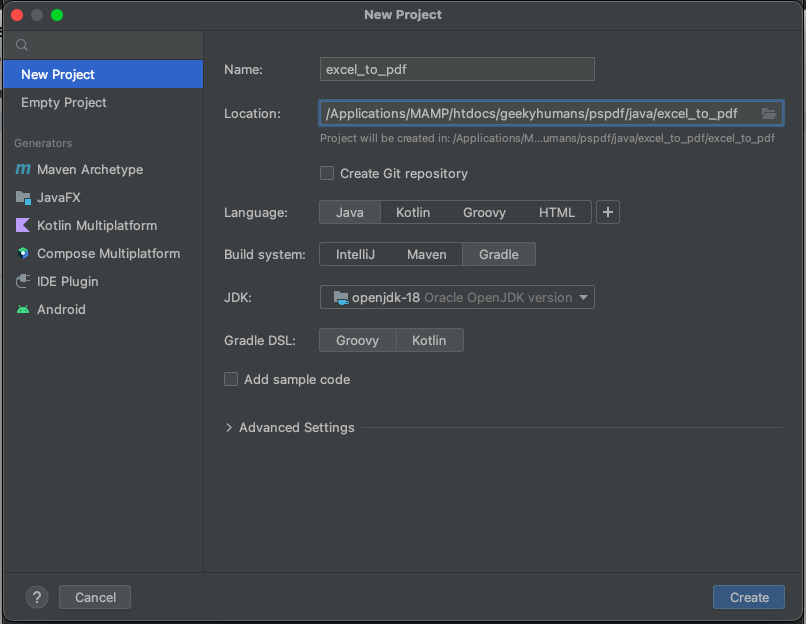
Create a new directory in your project. Right-click your project’s name and select New > Directory. Choose the src/main/java option. Create a class file inside the src/main/java folder called processor.java, and create two folders called input_documents and processed_documents in the root folder.
Place your Excel file in the input_documents folder. You can use our demo document as an example.
Your folder structure:
excel_to_pdf├── input_documents| └── document.xlsx├── processed_documents├── src| └── main| └── java| └── processor.javaStep 4 — Installing dependencies
Install two libraries:
- OkHttp — This library makes API requests.
- JSON — This library will parse the JSON payload.
Open the build.gradle file and add the following dependencies to your project:
dependencies { implementation 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:4.9.2' implementation 'org.json:json:20210307'}Click the Add Configuration button in IntelliJ IDEA to open a dropdown menu.
![]()
Select Application from the menu.
Fill the form with required details. Most fields are prefilled, but select java 18 in the module field and add -cp excel_to_pdf.main as the main class and Processor in the field below.
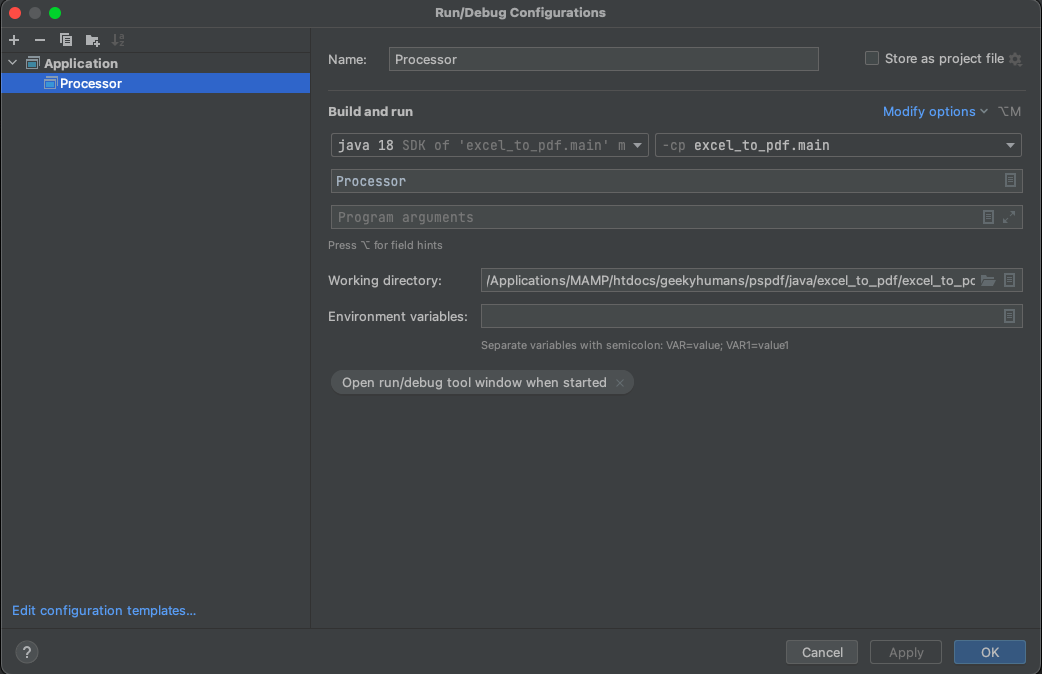
Click Apply to save settings.
Step 5 — Writing the code
Open the processor.java file and paste the code below into it:
package com.example.pspdfkit;
import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;import java.nio.file.FileSystems;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption;
import org.json.JSONArray;import org.json.JSONObject;
import okhttp3.MediaType;import okhttp3.MultipartBody;import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;import okhttp3.Request;import okhttp3.RequestBody;import okhttp3.Response;
public final class Processor { public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException { final RequestBody body = new MultipartBody.Builder() .setType(MultipartBody.FORM) .addFormDataPart( "file", "document.xlsx", RequestBody.create( MediaType.parse("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet"), new File("input_documents/document.xlsx") ) ) .addFormDataPart( "instructions", new JSONObject() .put("parts", new JSONArray() .put(new JSONObject() .put("file", "file") ) ).toString() ) .build();
final Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("https://api.nutrient.io/build") .method("POST", body) .addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY_HERE") .build();
final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient() .newBuilder() .build();
final Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
if (response.isSuccessful()) { Files.copy( response.body().byteStream(), FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("processed_documents/result.pdf"), StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING ); } else { // Handle the error. throw new IOException(response.body().string()); } }}Make sure to replace YOUR_API_KEY_HERE with your API key.
Code explanation
The code imports required packages and creates a class called processor. In the main function, you create the request body for the API call containing instructions for converting the Excel file to PDF. Then you call the API to process the instructions.
The execute() function processes the request variable. The API response saves to the processed_documents folder.
Output
To execute the code, click the Run button (the green arrow) next to the Processor field.
After successful execution, the result.pdf file appears in the processed_documents folder.
Final folder structure:
excel_to_pdf├── input_documents| └── document.xlsx├── processed_documents| └── result.pdf├── src| └── main| └── java| └── processor.javaAdditional resources
Work with Nutrient API using:
- Postman collection — Test API endpoints directly in Postman
- Zapier integration — Automate document workflows without code
- MCP Server — PDF automation for LLM applications
- JavaScript client — Official JavaScript/TypeScript library
Conclusion
This tutorial covered converting Excel files to PDF documents in Java applications using Nutrient’s Excel-to-PDF API.
With the same API token, you can perform other operations: merge multiple documents into a single PDF, add watermarks, and more. Sign up(opens in a new tab) for a free trial.
FAQ
No. Start with a free account that provides 200 credits for processing documents. Different operations consume different amounts of credits, so you can process varying numbers of documents depending on the operations you use.
Yes. Nutrient DWS Processor API maintains spreadsheet formatting, including fonts, colors, cell borders, and merged cells. Complex formulas are calculated and displayed as values in the PDF output.
The code requires Java 8 or higher. The example uses Java 18, but the OkHttp and JSON libraries are compatible with Java 8+. Verify your Java version with java -version.
Yes. Nutrient DWS Processor API converts all sheets in an Excel workbook to a single PDF document, with each sheet appearing as a separate page or set of pages depending on the sheet size.