Process documents with Document Engine and Golang
This guide walks you through the steps necessary to start Document Engine. It also shows you how to use it to process documents. By the end, you’ll be able to merge two PDF documents into one using Document Engine’s HTTP API with Golang.
Requirements
Document Engine is compatible with a range of platforms. Below is the list of supported operating systems.
- macOS:
- Ventura
- Monterey
- Mojave
- Catalina
- Big Sur
- Linux:
- Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS
- Ubuntu and Debian derivatives (such as Kubuntu, Xubuntu) are also supported
Processor requirements:
- 64-bit Intel (x86_64) processors
- ARM (AArch64) processors
Minimum system requirements:
- At least 4GB of RAM, regardless of the operating system
Installing Docker
Document Engine is distributed as a Docker container. To run it on your computer, you need to install a Docker runtime distribution for your operating system.
Install and start Docker Desktop for Mac. For detailed instructions, refer to the Docker website(opens in a new tab).
Install and start Docker Desktop for Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the Docker website(opens in a new tab).
Document Engine runs as a Linux container. If you’re using Docker Desktop for Windows, ensure it’s configured to work with Linux containers. For detailed steps, refer to the How do I switch between Windows and Linux containers? section in the Docker documentation(opens in a new tab). Users with Docker already set up might need to switch from Windows containers to Linux containers for compatibility.
Install and start Docker Engine. For detailed instructions on how to install Docker Engine for your Linux distribution, refer to the Docker website(opens in a new tab).
Once you finish installing Docker Engine, follow the instructions(opens in a new tab) to install Docker Compose.
Starting Document Engine
To start Document Engine, follow the steps below.
Open your terminal emulator.
Use the terminal emulator integrated with your code editor or IDE. Alternatively, you can use
Terminal.appor iTerm2(opens in a new tab).Use your code editor’s integrated terminal or PowerShell(opens in a new tab).
Use the terminal emulator integrated with your code editor or IDE, or the one bundled with your desktop environment.
Run the following command to start the Document Engine container:
docker run --rm -t -p 5000:5000 -e API_AUTH_TOKEN=secret pspdfkit/document-engine:1.14.0This command may take some time to complete depending on your internet connection speed, as it needs to pull the Docker image. You’ll know that Document Engine is successfully running when you see a message similar to the following in your terminal:
[info] 2024-02-05 18:56:45.286 Running Document Engine version 1.14.0Document Engine is now up and running!
Installing Golang
The interaction with Document Engine happens through its HTTP API. Documents and commands are sent in API request calls, and the resulting files are received in API response calls. API calls are invoked from the Go package, so you need to install Golang.
To install Golang:
Follow the instructions for your operating system on Golang’s download and installation page(opens in a new tab).
Go to any directory in your system using your terminal. Create a new directory called
merging-pdfsand go to the newly created directory:mkdir merging-pdfscd merging-pdfsCreate a new
gomodule by running the command below from themerging-pdfsdirectory. ReplaceYOUR-GITHUB-USERNAMEwith your actual GitHub username:go mod init github.com/YOUR-GITHUB-USERNAME/merging-pdfsCreate a new file in the directory called
merge.goand add the following content:package mainimport "fmt"func main() {fmt.Println("Hello World")}Run the file from your terminal with
go run merge.goto make sure everything is working properly.
Merging PDFs with Golang
If you don’t have any sample documents, download and use these files: cover.pdf and document.pdf
Replace the contents of the merge.go file with the code below. Replace /path/to/cover.pdf in lines 37 and 46, and replace /path/to/document.pdf in lines 59 and 68 with the actual paths to the example documents on your machine:
package main
import ( "bytes" "fmt" "io" "log" "mime/multipart" "net/http" "os" "path/filepath")
func main() { instructions := ` { "parts": [ { "file": "cover" }, { "file": "document" } ] } `
payload := &bytes.Buffer{} writer := multipart.NewWriter(payload)
err := writer.WriteField("instructions", instructions) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) }
// Replace "/path/to/cover.pdf". cover, err := os.Open("/path/to/cover.pdf") defer cover.Close()
if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
// Replace "/path/to/cover.pdf". coverPart, err := writer.CreateFormFile("cover", filepath.Base("/path/to/cover.pdf")) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
_, err = io.Copy(coverPart, cover) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
// Replace "/path/to/document.pdf". document, err := os.Open("/path/to/document.pdf") defer document.Close()
if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
// Replace "/path/to/document.pdf". documentPart, err := writer.CreateFormFile("document", filepath.Base("/path/to/document.pdf")) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
_, err = io.Copy(documentPart, document) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) return }
err = writer.Close() if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) return }
documentEngineUrl := "http://localhost:5000/api/build" method := "POST"
client := &http.Client{} req, err := http.NewRequest(method, documentEngineUrl, payload)
if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) return }
req.Header.Set("Authorization", "Token token=secret")
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", writer.FormDataContentType())
res, err := client.Do(req) if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) return } defer res.Body.Close()
output, err := os.Create("result.pdf")
log.Print(res) output.ReadFrom(res.Body)
if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) return }}To run the code, ensure you’re in the merging-pdfs directory and type the following command in your terminal:
go run merge.goMost of this code, up until the client.Do(req) statement, constructs a multipart request that’s sent to Document Engine. It includes two files — in this case, cover and document — and a list of instructions for Document Engine.
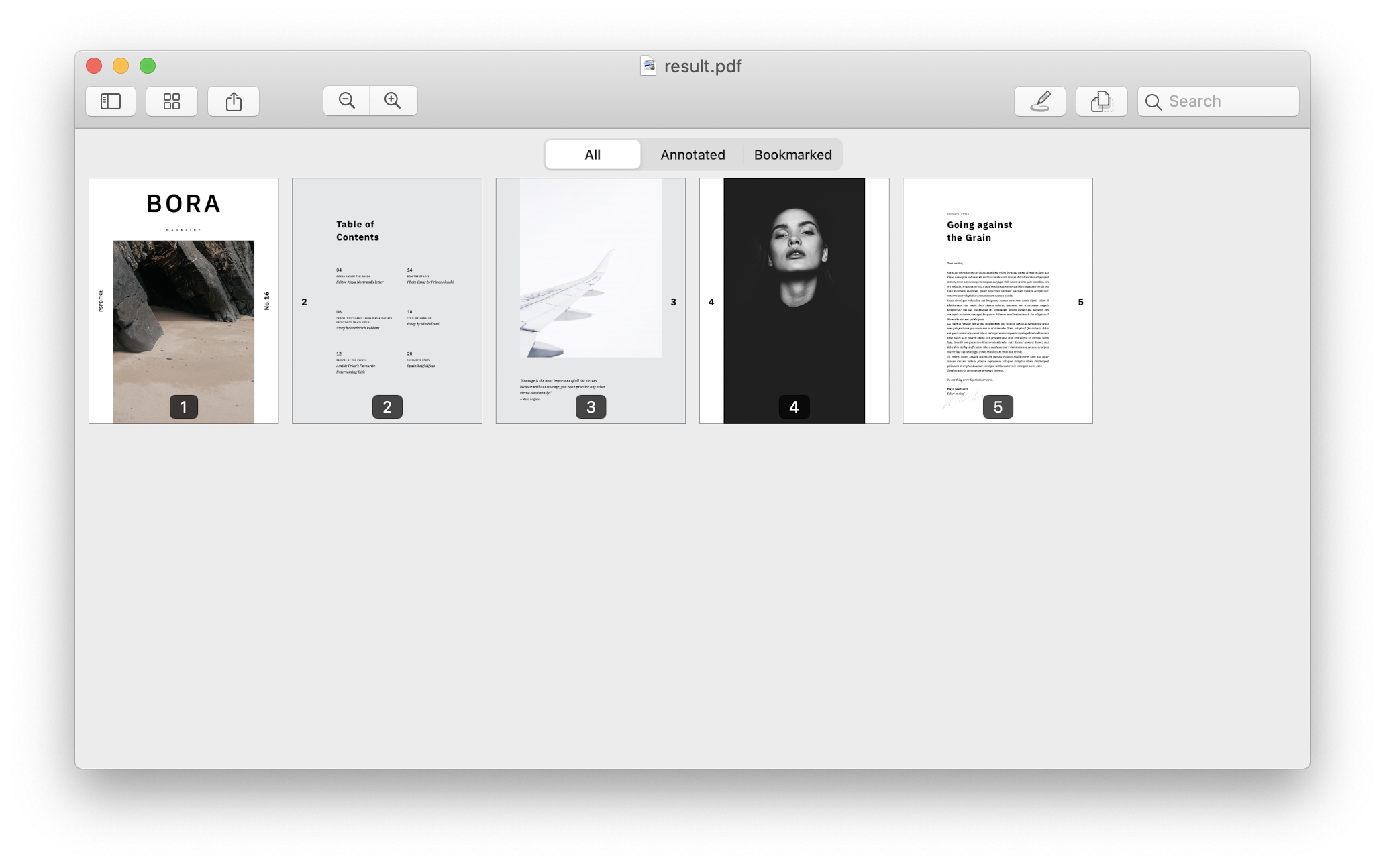
By default, Document Engine’s output for the /api/build endpoint is the result of merging all input documents or parts of the instructions.
The result of this code is a merged result.pdf file in the merging-pdfs directory.
To learn more about the various actions you can apply to PDFs using Document Engine, go to Document Engine’s API Reference.