Top five JavaScript PDF viewers for 2025
Table of contents

If you’re considering adding a JavaScript PDF viewer to your website or web application, you’re in the right place. This post will explore five JavaScript PDF viewers available in 2025:
The post will compare features, performance, pricing, and ideal use cases. Read on for a quick overview, and then dive deeper to choose the best viewer for your project.
Quick summary table of JavaScript PDF viewers
Here’s a quick summary of the best JavaScript PDF viewers available in 2025, including their key features, licensing, and supported frameworks.
| Viewer | Best for | License | Frameworks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Web SDK ★ Top pick | Enterprise and collaboration | Commercial | All (vanilla, React, Angular, Vue) |
| PDF.js | Lightweight apps | Free | All |
| react-pdf | React apps | Free | React |
| ngx-extended-pdf-viewer | Angular apps | Free | Angular |
| pdfvuer | Vue apps | Free | Vue.js |
What is a JavaScript PDF viewer?
A JavaScript PDF viewer renders PDF documents directly in the browser using client-side JavaScript. It can be embedded into webpages or JavaScript apps to display PDFs without requiring a server.
Most viewers offer a user-friendly interface with features like zoom, navigation, and text search. While many don’t support editing, some can be extended to handle annotations, form filling, signing, and more — making it easier to scale functionality without rewriting your code.
What is the cost of a JavaScript PDF viewer?
JavaScript PDF viewers range from free open source libraries (like PDF.js) to commercial SDKs (like Nutrient Web SDK).
- Free options are great for basic viewing but may lack support, advanced features, or performance optimization.
- Commercial options provide enterprise-grade features, scalability, and professional support — ideal for production apps and secure environments.
Nutrient Web SDK offers a fully featured free trial so you can evaluate before committing.
The five best JavaScript PDF viewers
This next section will provide an overview of the five best JavaScript PDF viewers.
Nutrient Web SDK: Best for enterprise and collaboration
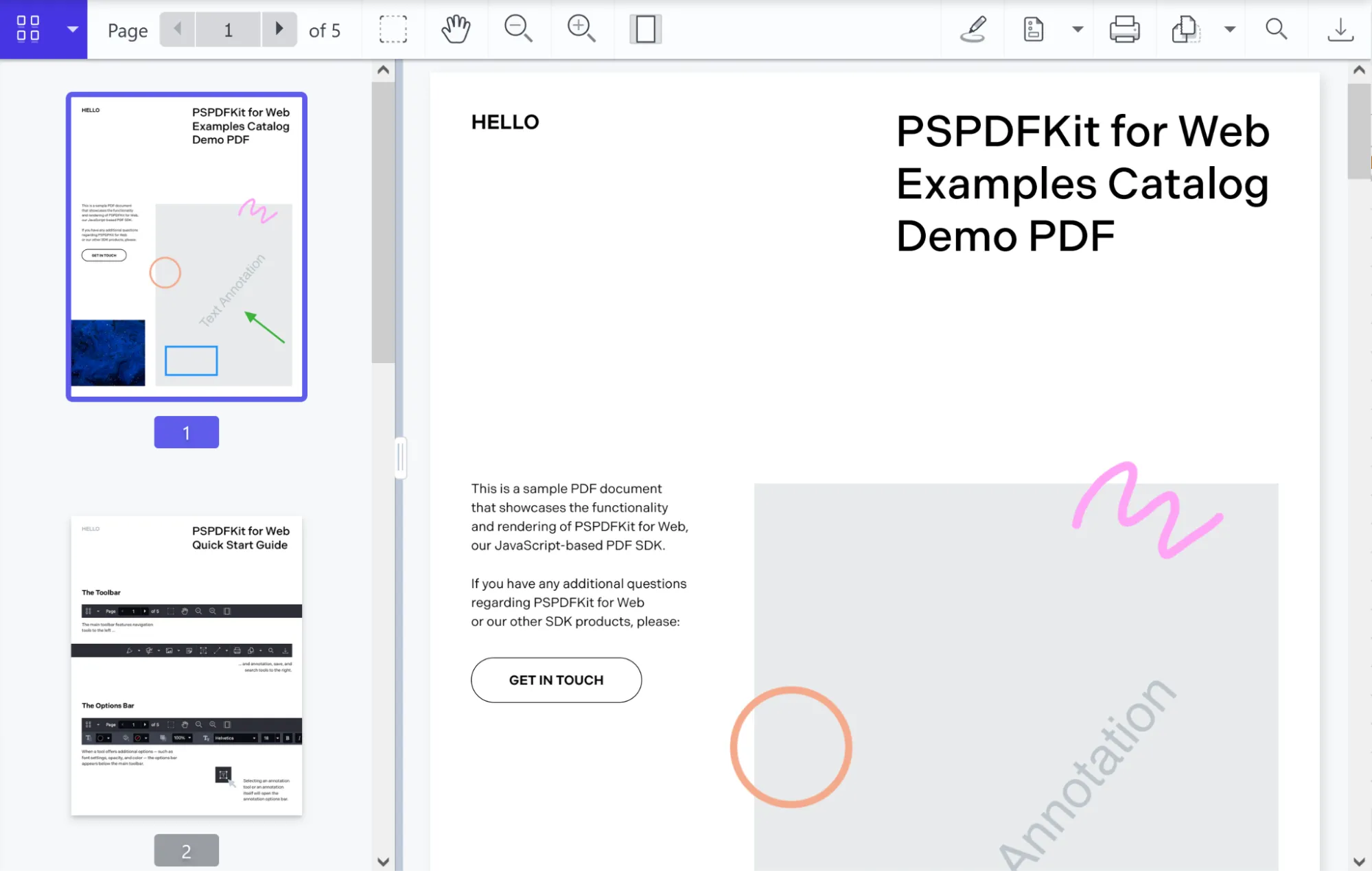
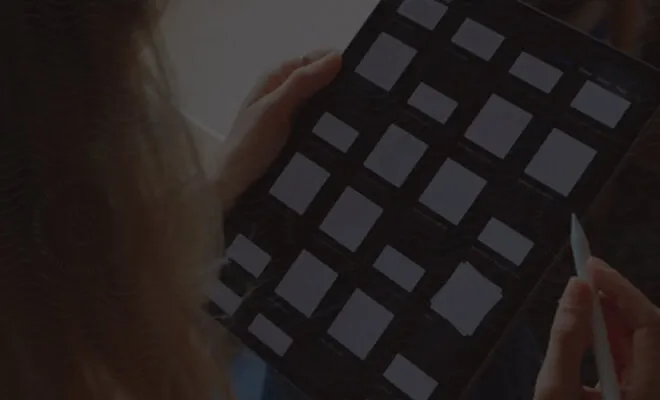
Since 2011, we at Nutrient have been working with the PDF specification and have developed one of the most comprehensive PDF SDKs available on the market. During that time, we’ve worked with many clients — including Disney, IBM, UBS, and Dropbox — to help them improve how their users work with PDF documents.
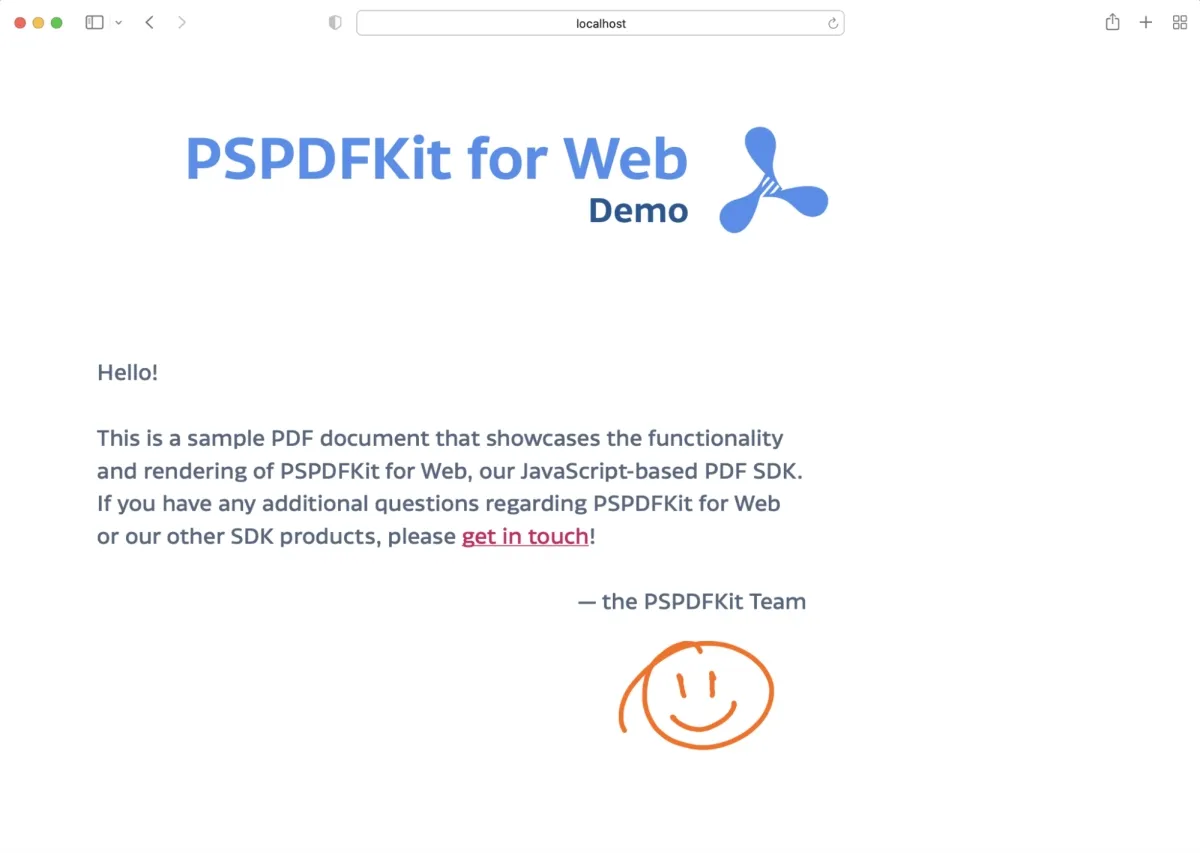
Nutrient Web SDK is our JavaScript PDF library — an SDK that offers PDF viewing, along with more than 30 other document processing tools (with many more tools planned). Try our web demo to see what it can do.
Example of our JavaScript PDF viewer
To demo our JavaScript PDF viewer, upload a PDF, JPG, PNG, or TIFF file by clicking Open Document under the Standalone option (if you don’t see this option, select Choose Example from the dropdown). Once your document is displayed in the viewer, try drawing freehand, adding a note, or applying a crop or an eSignature.
Key features
- Enterprise-grade security — Robust security controls, including encryption, access control, content protection, and audit-readiness.
- Customizable UI — Fully configurable viewer interface, toolbars, themes, keyboard shortcuts, and localization.
- High-fidelity rendering — Pixel-perfect PDF rendering based on a hardened Chromium engine with PDFium under the hood.
- Responsive and mobile-friendly — Automatically adapts to all screen sizes and orientations, with full touch and gesture support.
- Assistive tech and accessibility — Supports screen readers, keyboard navigation, and WCAG-compliant accessibility.
- Annotation tools — Create, edit, and manage ink, highlight, stamp, note, and shape annotations. Import/export XFDF or JSON.
- Form handling — Design and fill forms with AcroForm support, validations, autofill, and export to data formats.
- Digital signatures — Add and validate eSignatures and certificate-based digital signatures inline.
- AI-powered assistant — Use Nutrient AI Assistant to redact sensitive data, summarize text, extract insights, and generate smart actions.
- Document generation — Generate PDFs from templates or structured/unstructured data in real time.
- Document editing — Manipulate pages, merge/split files, crop, rotate, reorder, and apply visual changes.
- Redaction — Search and remove sensitive text or regions with permanent and audit-safe redaction tools.
- File format conversion — Convert PDFs to/from DOCX, XLSX, PNG, JPEG, TIFF, and more — on the fly.
- Real-time collaboration — Enable live collaboration with shared commenting, version control, and multi-user sessions.
- Thumbnail and bookmark management — Display page previews and manage hierarchical outlines and navigation.
- Full file format support — View and process:
- PDF, PDF/A
- Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint)
- Image formats (TIFF, JPG, PNG, WebP)
Pros
- Secure and compliant — Trusted by enterprises handling sensitive data (finance, legal, healthcare).
- Developer-friendly — Modular SDK with strong API documentation, code samples, and flexible integrations.
- Highly extensible — Supports advanced workflows like dynamic generation, real-time edits, and intelligent redaction.
Cons
- Not open source — Requires a commercial license for most production use cases. A fully featured free trial is available for evaluation.
Ideal use cases
- Enterprise apps requiring PDF editing, signing, and secure collaboration
- Internal portals with document workflows (HR, finance, compliance)
- Customer-facing dashboards that need embedded, branded PDF viewers
- Applications needing AI assistance for redaction or summarization
Pricing
Nutrient has simple and flexible pricing that’s based on a couple factors: the number of components and products you require, and the total number of users accessing the technology. Unlike other commercial libraries, we don’t install invasive trackers in your application, and we never send any information about your documents or users to external servers.
How to get started with Nutrient Web SDK
Create a project directory. Open your terminal and run:
Terminal window mkdir my-pdf-viewer && cd my-pdf-viewerInitialize your project. Create a Node.js project:
Terminal window npm init -yInstall the
@nutrient-sdk/viewerpackage:Terminal window npm install @nutrient-sdk/viewerCopy the SDK assets to a local
assetsdirectory:Terminal window mkdir assets && cp -R ./node_modules/@nutrient-sdk/viewer/dist/ ./assets/Rename the PDF you want to display to
document.pdfand place it in the root of your project directory. You can also use our demo PDF document for testing.Create the viewer HTML. Create an
index.htmlfile with the following content:<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><title>Nutrient PDF Viewer</title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /></head><body><div id="nutrient" style="width: 100%; height: 100vh;"></div><script type="module" src="index.js"></script></body></html>Initialize the viewer in JavaScript. Create an
index.jsfile:import "./assets/nutrient-viewer.js";const baseUrl = `${window.location.protocol}//${window.location.host}/assets/`;NutrientViewer.load({baseUrl,container: "#nutrient",document: "document.pdf",}).then((instance) => {console.log("Nutrient loaded", instance);}).catch((error) => {console.error(error.message);});This loads and mounts the Nutrient PDF viewer with your specified document.
Install a local static server and run it:
Terminal window npm install --global serveserve -l 8080 .Visit http://localhost:8080(opens in a new tab) to view your PDF viewer. You should see your PDF rendered inside the Nutrient Web SDK viewer.
If you prefer a video tutorial, you can watch our step-by-step guide.
Additional resources
For more details, check out our guides, code samples, and API documentation.
If you’re looking for related tutorials, you might find these posts helpful:
These resources will give you actionable insights for working with Nutrient in your projects.
Try Nutrient Web SDK free — no credit card required. Explore high-fidelity viewing, annotations, signing, and more.
PDF.js: Best for simple, open source needs

PDF.js(opens in a new tab) is a popular open source JavaScript library launched by Mozilla in 2011 and maintained by a community of more than 360 contributors. It has more than 42K GitHub stars and is used by Firefox to open PDFs natively in the browser.
- It has a good security track record, with Mozilla quickly patching vulnerabilities (learn more in the security advisories(opens in a new tab)).
- PDF.js doesn’t collect or transmit any information about users or documents.
- PDF.js offers a customizable viewer interface that can be themed via CSS or extended by modifying its source code or using the lower-level API.
- PDF.js supports rendering existing annotations, but it doesn’t support creating or editing them; there’s no built-in support for adding ink, text notes, or form data.
Supported file types
Pricing
PDF.js is free and open source, available under the Apache License 2.0(opens in a new tab).
Pros
- Open source — Free to use, with a strong community supporting it.
- Wide adoption — Widely used, especially in Firefox and other browsers.
- Customizable UI — Allows adjustments to match your app’s branding and user experience.
Cons
- Basic features — Limited to annotations and lacks advanced editing features.
- Rendering performance — May struggle with large or complex PDFs, especially on lower-end devices.
Use cases
- Basic PDF viewing — Ideal for apps that only need to display PDFs.
- Browsers and websites — Supported natively by Firefox, making it perfect for browser-based applications.
If you’d like to get started with PDF.js, here are some helpful tutorials to get you up and running:
- Complete guide to PDF.js: The leading JavaScript library for PDF rendering
- How to build a JavaScript PDF viewer with PDF.js
- How to build a React PDF viewer with PDF.js
- How to build a TypeScript PDF viewer with PDF.js
- How to build a Vue.js PDF viewer with PDF.js
- How to build an Angular PDF viewer with PDF.js
- How to build an Electron PDF viewer with PDF.js
react-pdf: Best for React developers
react-pdf(opens in a new tab) is a popular open source React component that renders PDF files using PDF.js. It’s maintained by an open source community with 53 contributors and has more than 7K GitHub stars.
- It leverages PDF.js for rendering, ensuring compatibility and performance.
- There were no known vulnerabilities when this blog was published. Any vulnerabilities in PDF.js will also affect react-pdf.
- It doesn’t collect or transmit any information about users or documents.
- The UI is minimal and requires further customization through APIs to meet your needs.
- The same features as PDF.js, such as annotations and form filling, are available in react-pdf.
Supported file types
Pricing
react-pdf is free and open source, available under the MIT license(opens in a new tab).
Pros
- React component — Specifically designed for React, making it easy to integrate.
- Uses PDF.js — Leverages PDF.js for rendering, ensuring compatibility.
- Flexible API — Provides an easy-to-use API for rendering individual pages and customizing the viewer.
Cons
- Basic UI — Requires further development for a more sophisticated interface.
- Performance on large documents — May experience performance issues with large or complex PDFs.
Use cases
- React projects — Ideal for React applications that need PDF display functionality.
- Single-page PDF viewing — Useful for apps displaying one PDF page at a time, such as documentation viewers.
Integration example
import { Document, Page } from "react-pdf";
function MyPDFViewer() { return ( <div> <Document file="/path/to/your/document.pdf"> <Page pageNumber={1} /> </Document> </div> );}When it’s crucial
- React-based apps — When building a React app and needing seamless PDF rendering.
- Single-page PDF display — Ideal for apps where only one PDF page is displayed at a time.
If you’d like to get started with react-pdf, here’s a helpful tutorial to get you up and running:
ngx-extended-pdf-viewer: Best for Angular apps
ngx-extended-pdf-viewer(opens in a new tab) is a popular open source Angular component that wraps PDF.js to enable seamless PDF viewing. Maintained by a community of 26 contributors, it has garnered more than 350 GitHub stars.
- At the time of publishing, no vulnerabilities were known. However, since it uses PDF.js under the hood, any vulnerabilities in PDF.js will also affect ngx-extended-pdf-viewer.
- It doesn’t collect or transmit any user or document data.
- The UI is similar to PDF.js and customizable via CSS theming and API configuration. The documentation(opens in a new tab) provides wizards to customize buttons, toolbars, sidebars, and thumbnails.
- Along with the features of PDF.js, it includes additional functionality such as prerendering, touch gestures, and events, for an improved user experience.
Supported file types
Pricing
ngx-extended-pdf-viewer is free and open source, available under the Apache License 2.0(opens in a new tab).
Pros
- Angular integration — Designed specifically for Angular, making it easy to use in Angular applications.
- PDF.js backend — Utilizes PDF.js for reliable rendering and compatibility.
- Enhanced features — Offers additional capabilities like touch gestures, prerendering, and event handling.
Cons
- Framework-specific — Limited to Angular projects, which restricts its use in other frameworks.
- Missing advanced tools — Lacks features like form filling and real-time collaboration.
Use cases
- Angular applications — Ideal for Angular-based apps requiring robust PDF viewing.
- Touchscreen support — Great for mobile and tablet apps with touch gesture and zooming functionality.
Integration example
<ngx-extended-pdf-viewer [src]="'/path/to/document.pdf'" [textLayer]="true" [showHandToolButton]="true" [showPresentationModeButton]="true" [showDownloadButton]="true"></ngx-extended-pdf-viewer>When it’s crucial
- Angular projects — Essential for Angular apps that require PDF viewing capabilities.
- Mobile and tablet optimization — Perfect for applications targeting touch-based devices.
If you’d like to get started with ngx-extended-pdf-viewer, here’s a helpful tutorial to get you up and running:
Try Nutrient Web SDK free — no credit card required. Explore high-fidelity viewing, annotations, signing, and more.
pdfvuer: Best for Vue apps
pdfvuer(opens in a new tab) is an open source Vue.js component that uses PDF.js for rendering PDF files. It has 19 contributors and more than 800 GitHub stars, and it’s available under the MIT license(opens in a new tab).
- No vulnerabilities were known at time of publishing, but it inherits any PDF.js issues.
- It doesn’t collect or transmit user or document data.
- Offers a basic UI, requiring customization via APIs.
- Provides the same features as PDF.js.
Supported file types
Pros
- Vue.js integration — Easy to use in Vue.js applications.
- Lightweight — Minimal, efficient PDF viewer.
Cons
- Basic UI — Requires additional customization.
- Limited features — No form filling or annotations.
Use cases
- Vue.js projects — Lightweight PDF viewer for Vue-based apps.
- Simple PDF display — Ideal for displaying PDFs without advanced features.
Integration example
<pdfvuer :src="'/path/to/your/document.pdf'" />If you’d like to get started with pdfvuer, here’s a helpful tutorial to get you up and running:
Comparison table
This table will help you identify the best option based on specific project needs, such as integration ease, available features, support options, performance, and the ideal use case.
| Feature | Nutrient Web SDK | PDF.js | React PDF | ngx-extended-pdf-viewer | pdfvuer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of integration | Moderate (advanced features) | Easy (requires minimal setup) | Easy (React-specific) | Moderate (Angular-specific) | Easy (Vue-specific) |
| Advanced features | Yes (annotations, form filling, signing, collaboration) | Basic (viewing only) | Basic (viewing only) | Yes (annotations, touch support) | Basic (viewing only) |
| Support availability | High (commercial support, enterprise-level) | Community-based (limited) | Community-based (limited) | Community-based (limited) | Community-based (limited) |
| Performance | Excellent (optimized for large files, enterprise-level) | Good (basic rendering, can struggle with large files) | Good (leverages PDF.js) | Good (optimized for Angular apps) | Good (optimized for Vue.js apps) |
| Best for small teams | No (requires paid license) | Yes (free, minimal setup) | Yes (free, minimal setup) | No (Angular-specific) | Yes (free, minimal setup) |
| Best for enterprise-grade projects | Yes (advanced features, real-time collaboration, high security) | No (limited features, basic viewer) | No (basic functionality) | No (Angular-specific) | No (basic functionality) |
| Ideal for lightweight apps | No (feature-rich, more complex) | Yes (simple, minimal setup) | Yes (simple, minimal setup) | Yes (lightweight Angular support) | Yes (lightweight Vue.js support) |
| Ideal for document collaboration | Yes (real-time annotations, sharing, signing) | No (limited to viewing) | No (limited to viewing) | Yes (annotations, touch support) | No (limited to viewing) |
Summary of recommendations
- Best for small teams:
- PDF.js, React PDF, and pdfvuer — All are free, easy to set up, and great for small teams needing a simple PDF viewer with basic features.
- Ideal for enterprise-grade projects:
- Nutrient Web SDK — Offers enterprise-level features like form filling, annotations, and real-time collaboration, making it perfect for large, secure, or collaborative applications.
- Best for lightweight apps:
- PDF.js, React PDF, and pdfvuer — These options are suitable for lightweight applications where PDF viewing is the only requirement, with minimal setup and no need for advanced features.
- Best for document collaboration:
- Nutrient Web SDK and ngx-extended-pdf-viewer — These libraries support annotation, form filling, and collaboration, making them ideal for apps that involve teamwork or document editing.
Common use cases for JavaScript PDF viewers
JavaScript PDF viewers do more than just display PDFs; they streamline workflows across various industries:
- Sharing documents — Embed PDFs directly into websites or apps for seamless access without downloads, enhancing user engagement.
- Financial and legal — Support collaborative workflows by displaying and annotating documents for reviews and approvals, keeping everyone updated with the latest version.
- Education — Facilitate sharing syllabi or assignments, enabling collaboration through in-document comments and edits synced across devices.
- Architecture and construction — Display blueprints, annotate changes, and measure directly in PDFs, even offline in remote locations.
- Document security — Protect sensitive content with restricted access, watermarks, and limited download or print options.
How to choose the right JavaScript PDF viewer
When selecting a JavaScript PDF viewer, consider these key factors:
- Security — Ensure the viewer is built on a secure PDF engine to protect against vulnerabilities.
Nutrient is designed with security in mind, using an optimized fork of PDFium(opens in a new tab) (the secure PDF engine used in Chromium) and undergoing independent third-party audits.
- Privacy — Verify that the library doesn’t collect or transmit user data.
Nutrient, for instance, doesn’t gather any information about users or documents, ensuring complete privacy.
- UI customization — Look for flexible customization options, from basic theming to advanced API integrations.
Nutrient offers robust customization tools, enabling seamless integration while protecting against UI-related vulnerabilities.
- Features — Ensure the viewer includes essential features like text search, zooming, navigation, and permissions.
Nutrient also supports advanced features like annotations, form filling, signing, and real-time collaboration, making it a scalable choice for evolving needs.
Nutrient’s thorough documentation and reliable support make it easier to extend its functionality and ensure long-term usability.
Final words
The best JavaScript PDF viewer for you depends entirely on your project’s requirements. While you should never make compromises in terms of security and privacy, you can be flexible with other factors and features.
If you only need to view PDFs and you don’t think your needs will expand in the future, then it’s a good idea to go with the most affordable solution. However, if you have — or predict having — more complex workflows, then the feature list becomes the crucial factor when selecting the right viewer.
If you want to test Nutrient’s JavaScript PDF viewer, you can get started with a free trial or play around with our web demo.
FAQ
A JavaScript PDF viewer is a library that renders PDF documents directly in web browsers, allowing users to view PDFs without needing an external PDF viewer.
Yes, many JavaScript PDF viewers offer UI customization options, ranging from simple CSS theming to advanced API integrations for more complex customizations.
No, most JavaScript PDF viewers are designed for viewing only. However, some may support basic editing features like annotations and form filling.
Yes, using an insecure PDF viewer can expose your app to vulnerabilities. It’s crucial to choose a secure and regularly updated library to mitigate risks.
JavaScript PDF viewers are widely used in industries like education, finance, and construction to display, share, and sometimes annotate PDF documents.
Most free PDF viewers support only basic rendering. If you’re building a business-critical app that needs annotations, eSignatures, or real-time collaboration, you’ll likely need a commercial solution.
Nutrient Web SDK offers a risk-free trial and scales flexibly with your team. It’s built for enterprise needs with no document tracking or cloud lock-in.







